Introduction
The emergence of cryptocurrencies, spearheaded by Bitcoin, has generated considerable interest across industries, transforming how we view and interact with money. As a decentralized, digital form of currency, cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain technology, allowing secure peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks. But how did this innovation come to be, and what are the implications for the future of finance?
In this article, we’ll explore the origins of cryptocurrencies, their current role in global finance, and their potential for the future, offering a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to understand this growing phenomenon.
The Origins of Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies emerged from a desire to create a decentralized form of money, independent of central authorities like governments or banks. Bitcoin, introduced in 2009 by an anonymous figure (or group) under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, was the first successful cryptocurrency to implement this vision.
The roots of cryptocurrency lie in the cryptographic methods that protect and verify transactions. Bitcoin’s underlying blockchain technology records all transactions on a public ledger, making it virtually tamper-proof and ensuring transparency. Other early cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin and Ethereum, soon followed, each offering unique technological advancements or use cases.
How Cryptocurrencies Work: The Blockchain Explained
At the heart of every cryptocurrency lies blockchain technology. A blockchain is a decentralized network of computers, known as nodes, that collectively verify and record transactions. When someone initiates a cryptocurrency transaction, that data is bundled into a “block” and added to the chain of previous transactions. These blocks are linked cryptographically, ensuring the system’s integrity.
The blockchain operates under a consensus mechanism, the most common being Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW, used by Bitcoin, involves miners solving complex mathematical problems to add blocks to the blockchain, while PoS allows users to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold.
In extremely basic terms: Imagine you have a big book where you write down everything you buy or sell. But instead of just one book, lots of people have a copy, and they all have to agree that what you wrote is true. This way, no one can cheat or change the book without everyone knowing. That’s what cryptocurrencies do! The “book” is called a blockchain, and the people who check it are like super smart computers working together to make sure everything is fair and safe.
Pros of Blockchain in Cryptocurrencies:
- Security: Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms make it highly secure.
- Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger, ensuring accountability.
- Efficiency: Cryptocurrencies offer near-instantaneous cross-border transactions.
Cons:
- Scalability: As more people use the network, transactions can slow down.
- Energy Consumption: PoW, in particular, requires enormous computing power, contributing to environmental concerns.
Cryptocurrencies and Financial Systems: A Shift in Paradigm
Traditional vs. Cryptocurrency Transactions
In traditional financial systems, central banks and financial institutions oversee the issuance and management of currency. Transactions are processed through intermediaries like banks, which take time and involve fees. Cryptocurrencies remove these intermediaries, allowing direct transactions between parties at a fraction of the cost and time.
This direct peer-to-peer transaction model is particularly appealing for individuals in countries with unstable economies or limited access to traditional banking. Cryptocurrencies are seen as a way to democratize finance, offering financial inclusion to millions of people worldwide.
Case Study: El Salvador’s Adoption of Bitcoin
In 2021, El Salvador became the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender. This move aimed to improve financial inclusion for the country’s unbanked population and reduce reliance on remittance services, which often charge high fees. However, the experiment has faced mixed reactions, with many citizens still preferring traditional money, and volatility remains a significant concern.
Cryptocurrency Market and Growth Data
Cryptocurrencies have experienced explosive growth in both adoption and value. As of 2024, the total cryptocurrency market capitalization is over $2 trillion, with Bitcoin comprising approximately 40% of that value.
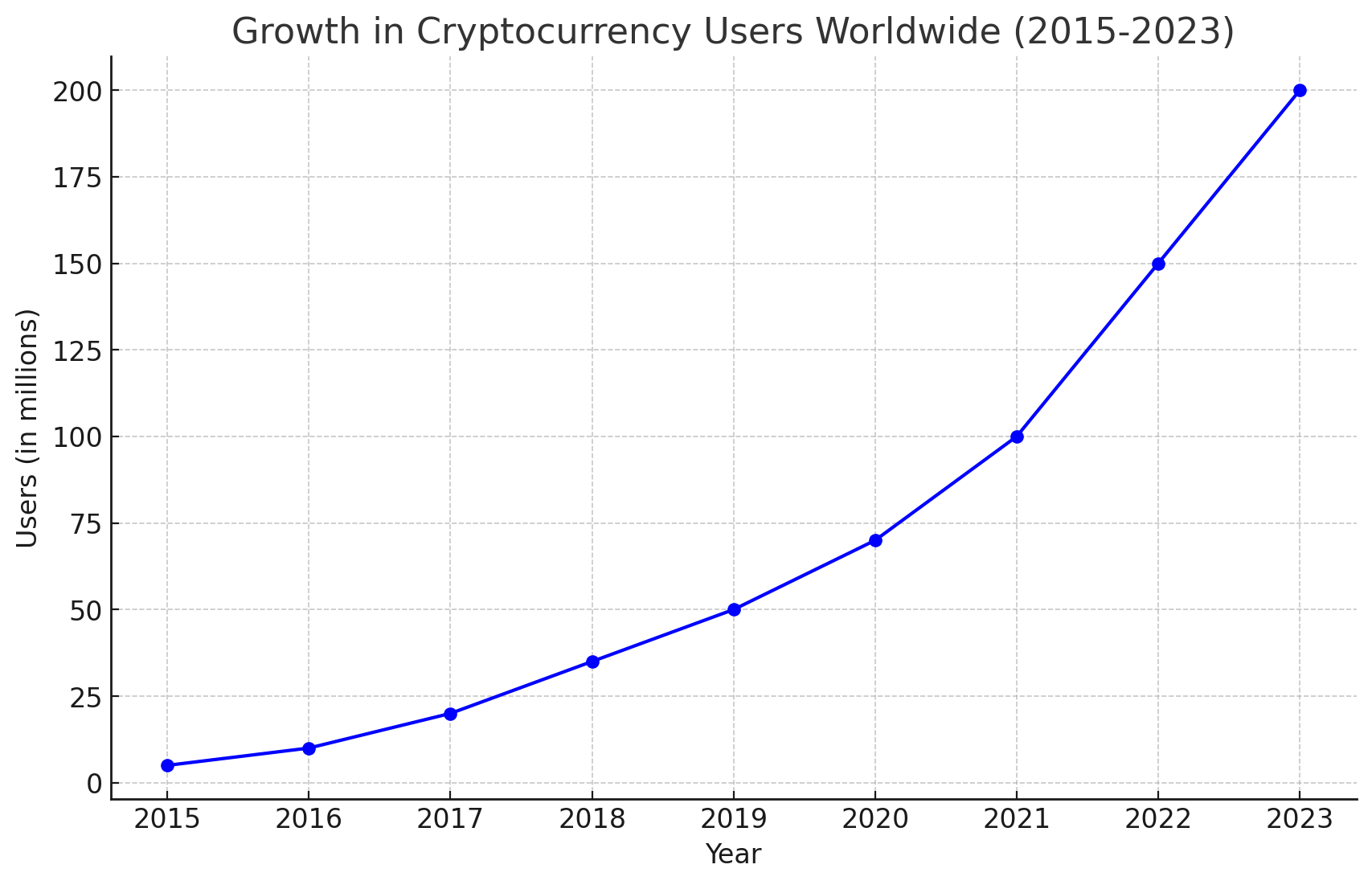
According to a study by the University of Cambridge, over 100 million people globally are using cryptocurrencies. The majority of adoption has been driven by:
- Retail investors seeking high returns.
- Institutional investors diversifying their portfolios.
- Businesses integrating cryptocurrency payments.
Key Advantages of Cryptocurrencies
- Decentralization: The absence of intermediaries such as central banks allows users more control over their assets.
- Financial Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies offer opportunities for individuals without access to traditional banking.
- Low Transaction Costs: Cryptocurrencies eliminate many fees associated with international payments and wire transfers.
- Inflation Hedge: With fixed supply caps (like Bitcoin’s 21 million limit), cryptocurrencies can act as a hedge against inflation.
Example: Bitcoin’s Role as “Digital Gold”
Many investors view Bitcoin as a store of value, akin to gold. Its limited supply makes it immune to inflationary pressures that affect fiat currencies. Historically, Bitcoin’s value has risen in times of economic uncertainty, mirroring gold’s role as a safe-haven asset.
Risks and Challenges
Despite their advantages, cryptocurrencies face several significant challenges:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies. Unclear regulations can deter investors and businesses from adopting these digital assets.
- The European Union’s proposed Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) seeks to create a harmonized regulatory framework across EU member states.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are notoriously volatile. Bitcoin, for example, saw its price drop from over $60,000 in 2021 to under $30,000 within months, before surging again.
- Volatility makes cryptocurrencies risky as a store of value or medium of exchange.
- Security Risks: Despite blockchain’s security, exchanges and wallets have been targets of cyberattacks. Notable hacks, such as the Mt. Gox exchange in 2014, saw billions of dollars worth of Bitcoin stolen.
- Environmental Concerns: The energy-intensive nature of Bitcoin mining, which relies on Proof of Work, has raised concerns about the environmental impact of cryptocurrencies. Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake in 2022 significantly reduced its energy consumption, offering a potential solution for other cryptocurrencies.
The Future of Cryptocurrencies
The future of cryptocurrencies remains uncertain, yet highly promising. While regulatory hurdles and volatility remain challenges, the increasing institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies suggests a bright future. Companies such as Tesla, MicroStrategy, and PayPal have embraced cryptocurrencies in various ways, with Tesla even accepting Bitcoin as payment for a time.
In addition to institutional interest, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, which aim to recreate traditional financial systems using blockchain technology, represents the next frontier for cryptocurrencies. DeFi applications could allow for decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries, further democratizing finance.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies are reshaping the financial landscape by offering new ways to store, transfer, and exchange value. While their future is uncertain, their potential for innovation and disruption in the global financial system cannot be ignored. As we move forward, understanding the intricacies of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology will be essential for anyone looking to navigate the evolving world of digital finance.
Sources:
- Nakamoto, S. (2009). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
- Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance. (2023). Global Cryptocurrency Adoption Report.
- European Parliament. (2024). Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA).

